基础常用类简介:Object、包装类、System、Scanner、BigInteger、BigDecimal、Math、Random、File、Date、SimpleDateFormat、Calendar、Arrays……
相关阅读:
目录
1 Object类
Object类是所有类的直接或间接父类,位于继承树的最顶层。任何类,如果没有书写extends显示继承某个类,都默认直接继承Object,否则为间接继承。在对象实例化的时候,最终找到的父类就是Object。
Object类提供无参构造方法,之所以提供这样的无参构造,是因为在子类对象实例化时都会默认调用父类中的无参构造方法,这样在定义类时即使没有明确定义父类为Object,读者也不会感觉代码的强制性要求。Object类中所定义的方法,是所有对象都具备的方法。
Object类型可以储存任何对象——作为参数,可接收任何对象;作为返回值,可返回任何对象。
1.1 基本实例方法
hashCode():返回该对象的哈希值。哈希值为根据对象的地址或字符串或数字使用hash算法计算出来的int值。
一般情况下相同对象返回相同哈希码。如果两个对象的哈希码值不同,那这两个对象一定不等;如果两个对象的哈希码值相同,不能确保这两个对象一定相等。
// s1和s2对象指向不相同,s1.hashCode() != s2.hashCode()
Student s1 = new Student();
Student s2 = new Student();
// s1和s3对象指向相同,s1.hashCode() == s2.hashCode()
Student s3 = s1;toString():返回该对象的字符串表示,默认为对象的类型 + @ + 内存地址值。在开发中,经常需要按照对象的属性得到相应的字符串表现形式,需要重写它。
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';
}
}clone():返回克隆对象的克隆。克隆对象对应的类需要实现Cloneable接口,否则会报错:java.lang.CloneNotSupportedExceptiongetClass():返回引用中存储的实际对象类型。通常用于判断两个引用中实际存储对象类型是否一致。
如何获取类的字节码文件对象?
类名.class: JVM将使用类装载器,将类装入内存(前提:类还未装入内存),不做类的初始化工作。返回Class的对象。Class.forName("类名字符串")(类名字符串:包名+类名):装入类,并做类的静态初始化,返回Class的对象。实例对象.getClass():对类进行静态初始化、非静态初始化;返回引用对象运行时真正所指的对象(因为子对象的引用可能会赋给父对象的引用变量中)所属的类的Class的对象。
notify()、wait():线程控制equals():比较两个对象地址是否相同。可进行重写来实现比较两个对象的内容是否相同。
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public boolean equals() {
if (this.name.equals(s.getName()) && this.age == s.getAge()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}1.2 Objects工具类
Objects工具类提供了上述成员方法的等价静态方法,这些方法是null-safe(空指针安全的)或null-tolerant(容忍空指针的),用于计算对象的hashcode、返回对象的字符串表示形式、比较两个对象。
例:在比较两个对象的时候,Object的equals方法容易抛出空指针异常,而Objects类中的equals静态方法就优化了这个问题,为public static boolean equals(Object a, Object b)。
public static boolean equals(Object a, Object b) {
return (a == b) || (a != null && a.equals(b));
}2 包装类
Java提供了两个类型系统:基本类型与引用类型。使用基本类型效率很高,然而很多时候需要创建对象使用,因为对象可以做更多的功能。
若想要基本类型像对象一样操作,可以使用基本类型对应的包装类。
| 基本类型 | 对应的包装类(位于java.lang包中) |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
2.1 装箱与拆箱
基本类型与对应的包装类对象之间来回转换的过程称为装箱与拆箱。
JDK5之前需要手动装箱、拆箱:
// 装箱:基本类型 → 引用类型
int num1 = 18;
Integer integer1 = new Integer(num1);
Integer integer2 = Integer.valueOf(num1);
// 拆箱:引用类型 → 基本类型
Integer integer3 = new Integer(100);
int num2 = integer3.intValue();由于经常要做基本类型与包装类之间的转换,后续版本中装箱、拆箱动作可以自动完成:
int age = 30;
// 自动装箱
Integer integer4 = age;
// 自动拆箱
int age2 = integer4;2.2 基本类型与字符串转换
除了Character类之外,其他所有包装类都具有parseXxx静态方法可以将字符串参数转换为对应的基本类型:
public static byte parseByte(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的byte基本类型。public static short parseShort(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的short基本类型。public static int parseInt(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的int基本类型。public static long parseLong(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的long基本类型。public static float parseFloat(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的float基本类型。public static double parseDouble(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的double基本类型。public static boolean parseBoolean(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的boolean基本类型。
// 1. 基本类型转成字符串
int n1 = 100;
// 1.1 使用+号(推荐)
String s1 = n1 + "";
// 1.2 使用Integer中的toString()方法
String s2 = Integer.toString(n1);
// 1.3 x为进制要求
String s2 = Integer.toString(n1, x);
// 2. 字符串转成基本类型
String str = "150";
// 2.1使用Integer.parseXXX();(推荐)
int n2 = Integer.parseInt(str);
// 2.2包装类型的构造器
Integer i = new Integer("2");
// 2.3返回保存指定的 String 的值的 Integer 对象
Integer integer2 = Integer.valueOf(num1);
// boolean 字符串形式转成基本类型,"true" ---> true
String str2 = "true";
boolean b1 = Boolean.parseBoolean(str2);3 System类
System类提供了一些与系统操作和属性相关的静态方法和属性。如:标准输入、输出和错误流,获取系统属性,退出程序,垃圾回收,获取当前时间,数组拷贝等。
3.1 标准流属性
static PrintStream out:标准输出流,用于将文本内容输出到控制台。static InputStream in:标准输入流,用于从控制台读取用户输入。static PrintStream err:标准错误输出流,用于输出错误信息到控制台。
3.2 静态方法
static void exit(int status):终止当前正在运行的 Java 虚拟机。status参数表示程序的退出状态。static long currentTimeMillis():返回当前时间的毫秒数,用于计算时间间隔等。static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length):将数组 src 中的一部分元素复制到数组 dest 中的指定位置。static String getProperty(String key):获取指定键的系统属性值。static String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue):获取指定键的系统属性值,如果没有找到则返回默认值。static void setProperty(String key, String value):设置指定键的系统属性值。static String getenv(String name):获取指定名称的环境变量值。static Map<String, String> getenv():获取所有环境变量的名称和值组成的映射。
public static void main(String[] args) {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("时间的毫秒数:" + time);
System.out.println("文件编码格式:" + System.getProperty("file.encoding"));
}4 标准输入读取类 ⭐️
4.1 Scanner类
Scanner类提供了多个构造方法,可以从不同的输入源(例如文件、字符串、流等)创建一个Scanner对象。用于简化从不同输入源(如键盘、文件等)读取数据的过程。
常用构造法:
new Scanner(System.in):从标准输入流读取数据
实例方法:
boolean hasNext()、String next():检测(默认以空白字符作为分隔符)、获取下一个标记(返回字符串)。boolean hasNextLine()、String nextLine():检测、获取下一行的内容(返回字符串)。- 检测、获取特定类型数据:
hasNextXxx、nextXxx(返回对应的基本类型数据)hasNextInt()、nextInt()hasNextDouble()、nextDouble()hasNextBoolean()、nextBoolean()- ……
void close():关闭 Scanner 对象。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String text = scanner.next();
System.out.println("您输入的内容是:" + text);
}算法题使用说明:
- 优点:代码简短
- 缺点:大量数据时效率低,且next()和nextLine()同时使用时容易出错(需要考虑空格和换行)
- 总结:少量数据时使用,且最好是纯数字,不建议用于处理字符串,易出错
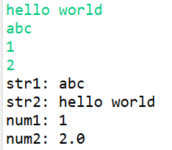
【例】读取各种类型数据
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerInput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str1 = sc.nextLine(); // 输入一行可包含空格的字符串, 回车结束
String str2 = sc.next(); // 输入一个字符串,遇到空格或换行时就停止读取
int num1 = sc.nextInt(); // 输入一个整数
double num2 = sc.nextDouble(); // 输入一个浮点数
//sc.close(); // 关闭,养成好习惯,也可以忽略
System.out.println("str1: " + str1);
System.out.println("str2: " + str2);
System.out.println("num1: " + num1);
System.out.println("num2: " + num2);
}
}
4.2 BufferedReader类
BufferedReader:从缓存区读取内容
常用构造法:
BufferedReader(Reader in):传入一个Reader(字符流)实例进行构造- 一般通过如下方式来构造:
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
- 一般通过如下方式来构造:
实例方法:
readLine():从缓存区读取一行内容,返回字符串
public class BufferedReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System.in为InputStream实例对象
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = null;
System.out.print("请输入内容:");
try {
str = reader.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("\n输入的内容为:" + str);
}
}
算法题使用说明:
- 优点:通过读取字符串类型,可以读入许多字符(字母、数字、其他等),因此可以进行格式化输入。同时在使用时,一般对于输入的每一行,各用一个String变量进行接收,再通过处理转为int等,读入思路比较明确(针对每一行)
- 缺点:代码略复杂,因为获得的是String类型,需要通过Interger的方法转为int和double类型,效率较StreamTokenizer等稍微差些。
【例】当需要一个序列数据时,先用String[]数组接收,再通过for循环存储到目标数组arr中。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class BufferedReaderInput {
private static BufferedReader bin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 输入
// 5
// 1 2 3 4 5
String line1 = bin.readLine(); // 5
int n = Integer.parseInt(line1);
String[] line2 = bin.readLine().split(" "); // 1 2 3 4 5 一次性输入完,再for存储
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(line2[i]);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
5 大数类
5.1 BigInteger类
位于java.math.BigInteger。不可变的任意精度的整数。
构造方法:
BigInteger(String s):通过字符串创建BigInteger对象
成员方法:
add(BigInteger bi):+subtract(BigInteger bi):-multiply(BigInteger bi):*divide(BigInteger bi):/
5.2 BigDecimal类
位于java.math.BigDecimal。不可变的、任意精度的有符号十进制数。
构造方法
BigDecimal(String s):通过字符创建BigDecimal对象
成员方法
add(BigDecimal bi):+subtract(BigDecimal bi):-multiply(BigDecimal bi):*divide(BigDecimal bi, x, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP):/(x为保留小数位数)
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(1.0);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(0.9);
BigDecimal sum = null;
sum = b1.add(b2);
sum = b1.subtract(b2);
sum = b1.multiply(b2);
sum = b1.divide(b2, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);6 Math类
Math工具类提供了一系列数学运算的静态方法
abs(int a):绝对值ceil(double d):向上取整floor(double d):向下取整max(int a, int b):最大值pow(double a, double b):a的b次幂random():生成[0.0,1.0]上的随机数round(float f):四舍五入(原理:在参数上加0.5再进行取整)sqrt(double d):算术平方根
int a = -10;
double d = 3.33;
int b = 5;
int absValue = Math.abs(a); // 获取a的绝对值
double ceilValue = Math.ceil(d); // 向上取整
double floorValue = Math.floor(d); // 向下取整
int maxValue = Math.max(a, b); // 获取最大值
double power = Math.pow(d, 2); // d的2次幂
double randomValue = Math.random(); // 生成0.0到1.0上的随机数
int roundValue = Math.round(d); // 四舍五入
double sqrtValue = Math.sqrt(d); // 算术平方根7 Random类
Random类用于生成随机数。只要两个Random对象的种子相同,而且方法的调用顺序也相同,产生的随机数相同。
构造方法:
Random():以当前时间毫秒值作为种子,创建Random对象Random(long seed):以指定种子创建Random对象
成员方法:
nextInt():生成1个int类型范围的随机数nextInt(int n):产生1个$[0,n-1]$范围内的随机数
/* 生成[0, n]上的数 */
// 法1:使用Math.random()静态方法
int res = (int)Math.random() * (n + 1)
// 法2:使用Random类对象
Random r = new Random();
int res = r.nextInt(n + 1);
/* 生成[n, m]上的随机数 */
// 法1:使用Math.random()静态方法
int res = n + (int)(Math.random() * (m + 1 - n));
// 法2:使用Random类对象
Random r = new Random();
int res = r.nextInt(m + 1 - n) + n;UUID:用于做数据库的id
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 效果:39eb10ce-e8be-49f5-a44b-bfd0aa8c81358 File类
File文件类以抽象的方式代表文件名和目录路径名。主要用于文件和目录的创建、文件的查找和文件的删除等。File对象代表磁盘中实际存在的文件和目录。
构造方法:
File(File parent, String child):通过给定的父抽象路径名和子路径名字符串创建一个新的File实例。File(String pathname):通过将给定路径名字符串转换成抽象路径名来创建一个新File实例。File(String parent, String child):根据父路径名字符串和子路径名字符串创建一个新File实例。File(URI url):通过将给定的文件URI转换成一个抽象路径名来创建一个新的File实例。
// 通过给定的父路径名和子路径名字符串创建一个新的File实例。
File parent = new File("C:/Users");
String child = "Documents";
File file1 = new File(parent, child);
// 通过给定路径名字符串转换成抽象路径名来创建一个新File实例。
String pathname = "C:/Users/Public";
File file2 = new File(pathname);
// 根据父路径名字符串和子路径名字符串创建一个新File实例。
String parentPath = "C:/Users";
String childPath = "Downloads";
File file3 = new File(parentPath, childPath);
// 通过将给定的文件URI转换成一个抽象路径名来创建一个新的File实例。
URI uri = new File("C:/Users/Public/Documents").toURI();
File file4 = new File(uri);添加文件:
public boolean mkdir():创建此抽象路径名指定的目录。public boolean mkdirs():创建此抽象路径名指定的目录,包括创建必需但不存在的父目录。
查看文件:
public File[] listFiles():返回一个抽象路径名数组,这些路径名表示此抽象路径名所表示目录中的文件。
修改文件:
public boolean renameTo(File dest):重新命名此抽象路径名表示的文件。
删除文件:
public boolean delete():删除此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录。
// 创建文件夹
File folder = new File("testFolder");
if (folder.mkdir()) {
System.out.println("Folder created successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Failed to create folder.");
}
// 创建多层文件夹
File multiLevelFolder = new File("multiLevelFolder/test");
if (multiLevelFolder.mkdirs()) {
System.out.println("Multi-level folder created successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Failed to create multi-level folder.");
}
// 查看文件
File directory = new File("directory");
File[] files = directory.listFiles();
if (files != null) {
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file.getName());
}
}
// 修改文件名
File oldFile = new File("oldFile.txt");
File newFile = new File("newFile.txt");
if (oldFile.renameTo(newFile)) {
System.out.println("File renamed successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Failed to rename file.");
}
// 删除文件
File fileToDelete = new File("fileToDelete.txt");
if (fileToDelete.delete()) {
System.out.println("File deleted successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Failed to delete file.");
}9 Date类(旧版)
已过时,新版日期时间类详见:java.time日期/时间API包简介
9.1 Date
表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒值
构造方法:
Date():以当前时间毫秒值创建Date对象Date(long time):以指定的毫秒值创建Date对象(0表示1970:01:01 08:00:00)
成员方法:
long getTime():获取Date对象的毫秒值setTime(long time):设置Data对象的毫秒值
Date currentDate = new Date(); // 以当前时间毫秒值创建Date对象
Date specifiedDate = new Date(1000000000000L); // 以指定的毫秒值创建Date对象
long currentTimeMillis = currentDate.getTime(); // 获取Date对象的毫秒值
specifiedDate.setTime(2000000000000L); // 设置Data对象的毫秒值9.2 SimpleDateFormat
将日期时间类Date转换为自定义日期时间格式(格式化)。
标识字母(区分大小写):yMdHms —— 年月日时分秒
构造方法:
SimpleDateFormat():以默认模式创建对象SimpleDateFormat(String pattern):以指定模式创建对象
成员方法:
String format(Date date):格式化Date parse(String time):解析格式化
// 创建日期对象
Date date = new Date();
// 创建日期格式化解析对象
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// 调用格式化方法
String time = format.format(date);
// 打印结果
System.out.println(time); // 结果:2022-05-10 09:46:15// 创建日期格式化解析对象
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// 自定义时间
String str = "2020-05-10 09:46:15";
// 调用解析方法,返回date对象,抛出ParseException异常
Date date = format.parse(str);
// 打印结果
System.out.println(date); // 结果:Sun May 10 09:46:15 CST 20209.3 Calendar
Calendar日历类为抽象类(不可实例化),包含特定瞬间与一组字段,并为获取或者操作日历字段及其之间的转换提供了一些方法。
西方星期的开始为周日,中国为周一。
在Calendar类中,月份的表示是以0-11代表1-12月。
日期是有大小关系的,时间靠后,时间越大。
静态方法:
static Calender getInstance():以默认时区和语言创建日历
实例方法(调用上述方法获取对象后才可使用):
int get(int field):获取指定字段的日历值set(int field, int value):给指定的日历字段设置指定的值set(int year, int month, int date):设置年月日Date getTime():获取日历对象的Date日期setTime(Date d):设置日历对象的日期add(int field, int amount):对指定的日历字段添加指定的值
| 字段值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
YEAR |
年 |
MONTH |
月(从0开始) |
DAY_OF_MONTH |
月中的天(几号) |
HOUR |
时(12小时制) |
HOUR_OF_DAY |
时(24小时制) |
MINUTE |
分 |
SECOND |
秒 |
DAY_OF_WEEK |
星期几(周日为1) |
/* get/set */
// 获取日历类对象
Calendar time = Calendar.getInstance();
// 获取年
int year = time.get(Calendar.YEAR);
// 获取月
int month = time.get(Calendar.MONTH);
// 获取日
int day = time.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
// 获取时
int hour = time.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
// 获取分
int minute = time.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
// 获取秒
int second = time.get(Calendar.SECOND);
// 更改时间
time.set(Calendar.YEAR,2003);/* add */
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 2); // 加2天
cal.add(Calendar.YEAR, -3); // 减3年10 Arrays类
用于操作数组的工具类
/* 将指定序列转为List列表 */
static <T> List<T> asList(T... a)
/* 排序 */
static void sort(Object[] a)
static void sort(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) // from...to 左闭右开
static <T> void sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) // 自定义比较规则
/* 二分查找 */
static int binarySearch(Object[] a, Object key)
static int binarySearch(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, Object key)
/* 判断两个数组中的元素是否一一对应相等 */
static boolean equals(Object[] a, Object[] b)
/* 填充数组 */
static void fill(Object[] a, Object val)
/* 复制数组,需设置复制的长度 */
static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength)
/* 将某个范围内的元素复制到新的数组中 */
static <T> T[] copyOfRange(T[] original, int fromIndex, int toIndex)
/* 转换为字符串形式 */
static String toString(Object[] a)
static String deepToString(Object[] a) // 递归转换高维数组
《Java常用基础类总结》有1条评论