常用算法代码模板(Java)——数据结构:链表、栈、队列、单调队列、模式匹配、Trie树、并查集、堆、哈希
Java算法模板系列
目录
1 链表
用链式前向星(静态链表)实现链表的定义、遍历与增删改查。
1.1 单链表
无头单链表。元素结点地址idx从0开始分配,表尾空指针记为-1。

public class SingleLinkedList {
static final int N = 100010;
static int head; // 无头单链表的头指针
static int[] e = new int[N]; // e[i]存储结点i的值
static int[] ne = new int[N]; // ne[i]指向结点i的后继
static int idx; // idx为分配给结点的"地址"
// 初始化
public static void init() {
head = -1; // 头指针初始为-1
idx = 0; // 这里设定第1个插入的结点在0号下标
}
// 头插一个数x
public static void insertHead(int x) {
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = head; // 后继为开始结点
head = idx++;
}
// 在结点k之后插入一个数x
public static void insert(int k, int x) {
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k]; // 后继为k的后继
ne[k] = idx++;
}
// 删除头结点(需保证链表非空)
public static void removeHead() {
head = ne[head];
}
// 删除结点k之后的结点
public static void remove(int k) {
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ...
// 遍历整条链表
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int u = e[i];
// ...
}
}
}1.2 双链表
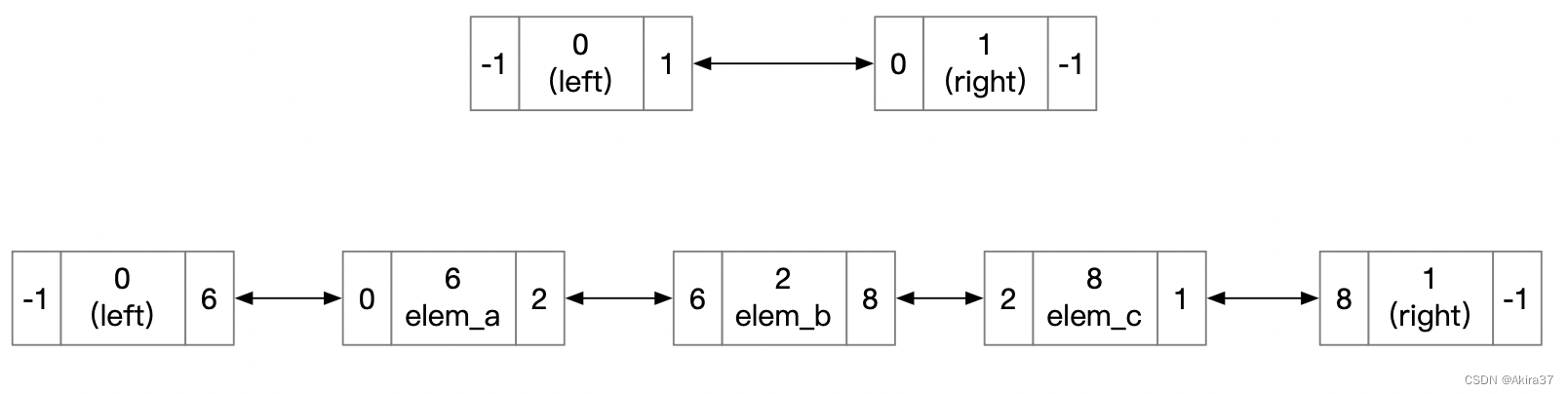
带头循环双链表。规定0是头结点/左端点,只有后继;1是尾结点/右端点,只有前驱。元素结点地址idx从2开始分配,每个元素结点都不含空指针。
对于删除操作,为避免繁杂通常不直接将结点移出链表,而是通过开bool数组st[]标记结点来实现,st[i]记录结点i是否被删除。
也可用来实现二叉树的二叉链表,此时无需再设循环的头结点。
public class DoubleLinkedList {
static final int N = 100010;
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] l = new int[N]; // l[i]、r[i]分别指向结点i的前驱、后继
static int[] r = new int[N]; // 特殊规定:0为头结点/左端点,只有后继;1为尾结点/右端点,只有前驱
static int idx;
// 初始化
public static void init() {
r[0] = 1; // 左右端点分别指向对方
l[1] = 0;
idx = 2; // 第1个结点从下标2开始存储
}
// 在结点k的右边插入一个数x
public static void insertR(int k, int x) {
e[idx] = x;
l[idx] = k; // 前驱为k
r[idx] = r[k]; // 后继为k的后继
l[r[k]] = idx; // k后继的前驱、k的后继(须最后修改)即为该结点
r[k] = idx++;
}
// 在结点k的左边插入一个数x
public static void insertL(int k, int x) {
insertR(l[k], x); // 等价于在结点k的前驱(l[k])的右边插入
}
// 删除结点k
public static void remove(int k) {
l[r[k]] = l[k];
r[l[k]] = r[k];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ...
// 遍历整条链表
for (int i = r[0]; i != 1; i = r[i]) {
int u = e[i];
// ...
}
}
}2 栈
FILO。手工数组建栈可以实现对栈内元素的随机存取。
public class Stack {
static final int N = 100010;
static int[] stk = new int[N]; // [0 ... N-1]
static int tt = -1; // 栈顶指针,初始指向-1
// 栈顶入栈一个数
public static void push(int x) {
stk[++tt] = x;
}
// 栈顶出栈一个数
public static void pop() {
tt--;
}
// 获取栈顶的值
public static int getTop() {
return stk[tt];
}
// 判断栈是否为空
public static boolean isEmpty() {
return tt != -1;
}
}3 队列
FIFO
3.1 非循环队列
手工建立的非循环队列队中元素不会被覆盖,由此可以实现对队内历史元素的遍历与随机存取,或根据指针判断某些性质(如拓扑序列)。
class LinearQueue {
static final int N = 100010;
static int[] q = new int[N]; // [0 ... N-1]
static int hh = 0; // 队头初始为0
static int tt = -1; // 队尾初始和栈顶一样为-1
// 队尾入队一个数
public static void enqueue(int x) {
q[++tt] = x;
}
// 队头出队一个数
public static void dequeue() {
hh++;
}
// 获取队头的值
public static int getFront() {
return q[hh];
}
// 获取队尾的值
public static int getRear() {
return q[tt];
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public static boolean isEmpty() {
return hh <= tt;
}
}3.2 循环队列
public class CircularQueue {
static final int N = 100010;
static int[] q = new int[N]; // [0 ... N-1]
static int hh = 0; // 队头和队尾指针初始均为0
static int tt = 0;
// 队尾入队一个数
public static void enqueue(int x) {
q[tt++] = x;
if (tt == N) tt = 0;
}
// 队头出队一个数
public static void dequeue() {
hh++;
if (hh == N) hh = 0;
}
// 获取队头的值
public static int getFront() {
return q[hh];
}
// 获取队尾的值
public static int getRear() {
return q[tt];
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public static boolean isEmpty() {
return hh != tt;
}
}4 单调队列
核心思想:及时弹出必不会作为答案的数,使得容器内各所指元素始终单调
4.1 单调栈
常见模型:找出数列中每个数左边离它最近的比它大/小的数
【例】输出数组a[1 ... n]中每个数左边离它最近的比它小的数,不存在则输出-1
public class MonotonicStack {
static final int N = 100010;
static int[] stk = new int[N]; // 栈中存储数组元素下标
static int tt = -1;
// 输出数组a[1 ... n]中每个数左边离它最近的比它小的数,不存在则输出-1
public static void printNums(int[] a, int n) {
// 思想:若a[x] >= a[y] (x < y),则a[x]必不会是任何一数的答案,可直接剔除
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 双指针算法,i是子区间右端点
while (tt != -1 && a[stk[tt]] >= a[i]) {
tt--; // 弹出既大又"远"的数
}
if (tt != -1) {
System.out.print(a[stk[tt]] + " "); // 输出栈顶元素
} else {
System.out.print("-1 "); // 输出-1
}
stk[++tt] = i; // 入栈当前元素下标
}
}
}4.2 单调队列
常见模型:找出滑动窗口中的最大值/最小值
【例】设数组a[1 ... n]中的滑动窗口长度为k,输出滑动窗口每次前移时窗口内的最小值
public class MonotonicQueue {
static final int N = 100010;
static int[] q = new int[N]; // 队列(双端队列)中存储数组元素下标
static int hh = 0;
static int tt = -1;
// 设数组a[1 ... n]中的滑动窗口长度为k,输出滑动窗口每次前移时窗口内的最小值
public static void printMinsOfSlidingWindow(int[] a, int n, int k) {
// 思想:同单调栈,且应输出的最值在队头(单调)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 双指针算法,i是子区间右端点
while (hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh]) {
hh++; // 判断队头是否滑出窗口
}
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >= a[i]) {
tt--; // 同单调栈,队尾弹出既大又"远"的数
}
q[++tt] = i; // 先将 i 从队尾入队
if (i + 1 >= k) {
System.out.print(a[q[hh]] + " "); // 当窗口长度达到要求时才输出
}
}
}
}5 模式匹配
5.1 暴力匹配
时间复杂度:$O(n\cdot m)$
public class BruteForce {
static String s; // 主串
static String p; // 模式串
public static void bruteForce() {
if (s.contains(p)) {
// ... 进行匹配成功后的操作
}
}
}5.2 KMP
next数组:$\text{next}[i]=$ 以 $i$ 为终点的最大公共前后缀(此处规定包含 $i$ )的长度
时间复杂度:$O(n+m)$
public class KMP {
static final int N = 100010;
static char[] s = new char[N]; // 主串 s[1 ... n]
static char[] p = new char[N]; // 模式串 p[1 ... m](必须从下标 1 开始存储字符)
static int n; // 主串长度为n
static int m; // 模式串长度为m
static int[] ne = new int[N]; // next 数组
// 初始化主串和模式串
public static void initStr() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
sc.next(); // 读取不带空格的字符串作为主串
s = (" " + sc.next()).toCharArray(); // 从下标1开始读取主串
p = (" " + sc.next()).toCharArray(); // 从下标1开始读取模式串
n = s.length - 1; // 获取主串有效存储长度 (s[0]用于填充)
m = p.length - 1; // 获取模式串有效存储长度 (p[0]用于填充)
}
// 求模式串p的next数组:p对p自己作KMP匹配
public static void initNext() {
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= m; i++) { // ne[1]=0,故i从2开始遍历
while (j > 0 && p[i] != p[j + 1]) {
j = ne[j]; // j回溯
}
if (p[i] == p[j + 1]) {
j++; // 匹配成功则表明得到了以当前i为终点的最大公共前后缀的长度
}
ne[i] = j; // 记录next数组
}
}
// KMP匹配
public static void kmp() {
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= n; i++) { // 始终与j的下一位 (j + 1) 作匹配
while (j > 0 && s[i] != p[j + 1]) {
j = ne[j]; // j回溯
}
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) {
j++; // 匹配成功时 j 走至下一位
}
if (j == m) { // 匹配成功的操作
// ... 进行匹配成功后的操作
j = ne[j]; // 若要求找到所有匹配点,则 j 继续回溯、匹配
}
}
}
}6 Trie树
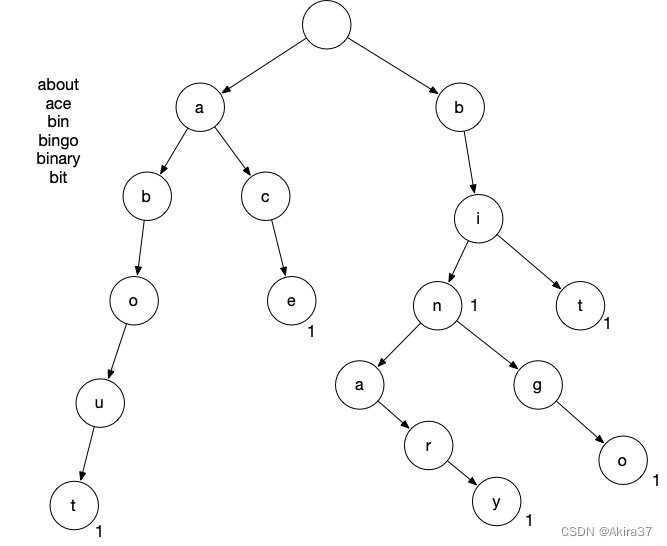
字典树(Retrieval Tree, Trie Tree)用于高效存储和查找字符串集合。
AC自动机为追加了fail指针的Trie树,算法思想参考KMP。
public class TrieTree {
static final int N = 100010;
static int[][] son = new int[N][26]; // son[p][u]记录结点p的第u个子结点
static int[] cnt = new int[N]; // cnt[p]存储以结点p结尾的单词数量
static int idx = 0; // idx初始为0(0号点既是根结点,又是空结点)
// 插入一个字符串
public static void insert(String str) {
int p = 0; // 从根结点0起遍历Trie的指针
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
int u = str.charAt(i) - 'a'; // 将字符转换为对应的索引
if (son[p][u] == 0) {
son[p][u] = ++idx; // 不存在则创建该子结点
}
p = son[p][u]; // 更新指针走向当前子结点
}
cnt[p]++; // p最终指向字符串末尾字母,p计数器自增
}
// 查询字符串出现的次数
public static int query(String str) {
int p = 0; // 从根结点开始
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
int u = str.charAt(i) - 'a'; // 将字符转换为对应的索引
if (son[p][u] == 0) {
return 0; // 不存在则直接返回0
}
p = son[p][u]; // 更新指针至下一个结点
}
return cnt[p]; // p最终指向字符串末尾字母,返回数量
}
}7 并查集
使用树的双亲表示法顺序存储,p[x]存储结点x的父结点(经过路径更新后变为该结点所属集合的根结点/祖宗结点)。若p[x] == x(或find(x) == x),则x为该集合的根结点。
判断结点a和b是否在同一集合:find(a) == find(b)
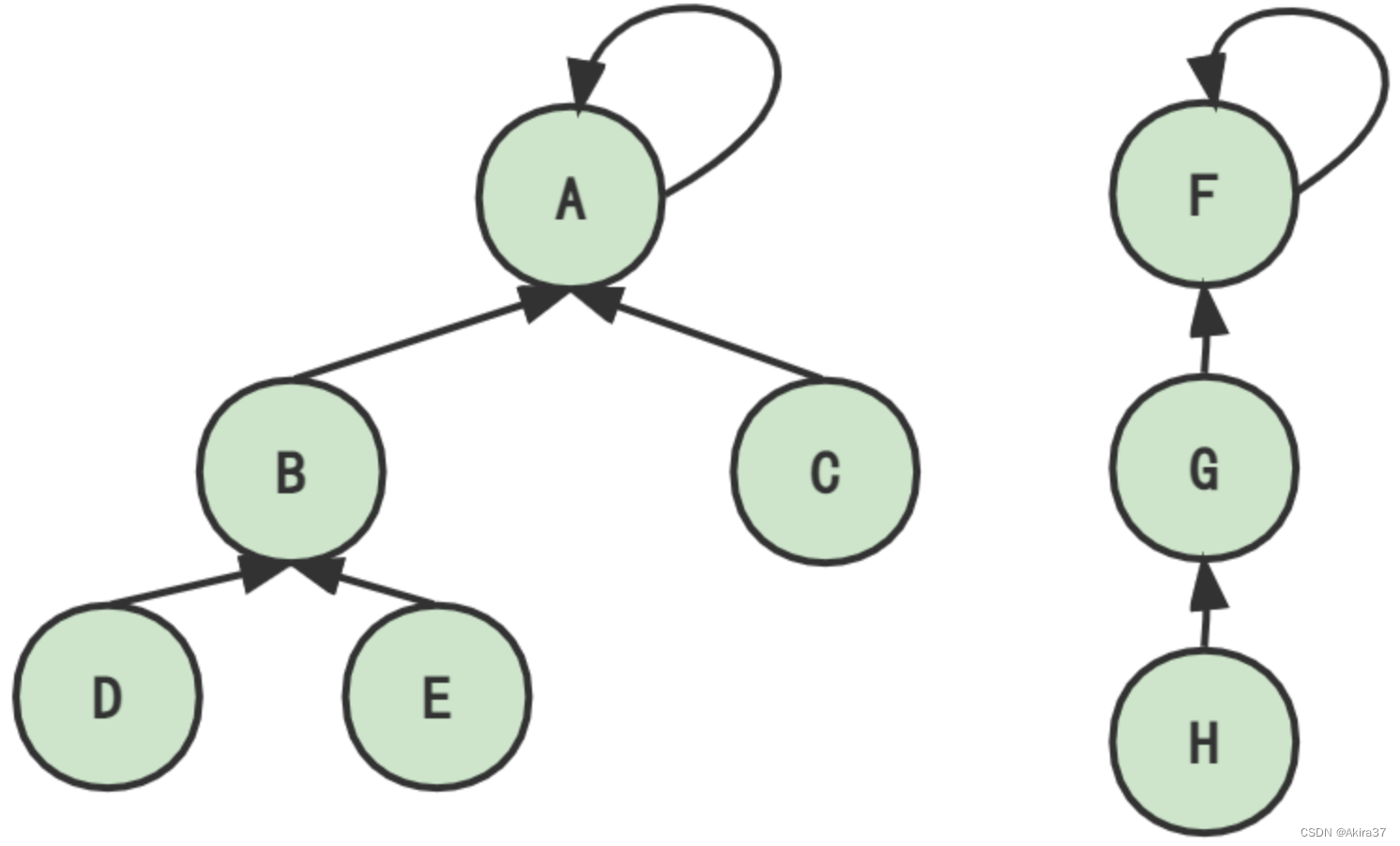
7.1 朴素并查集
public class SimpleDisjointSet {
static final int N = 100010;
static int n;
static int[] p = new int[N]; // p[1 ... n],p[i]存储结点i的祖先(路径压缩后则为根结点)
// 初始化
public static void init() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = i;
}
}
// 并查集核心操作:返回结点x所属集合的根结点,并进行路径压缩
public static int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
// 合并结点a和b所在集合:将a并至b
public static void union(int a, int b) {
p[find(a)] = find(b); // 将a的根接在b的根之后
}
}7.2 维护集合大小的并查集
结点a所属集合的大小:cnt[find(a)]
public class DisjointSetWithSize {
static final int N = 100010;
static int n;
static int[] p = new int[N];
static int[] cnt = new int[N]; // cnt[i]存储根结点i的集合中结点数(仅根结点的cnt有意义)
// 初始化
public static void init() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = i;
cnt[i] = 1; // 初始化各结点为根,其所属集合大小为1
}
}
// 并查集核心操作
public static int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
// 合并结点a和b所在集合:将a并至b
public static void union(int a, int b) {
if (find(a) == find(b)) return; // 若已在同一集合内则跳过
cnt[find(b)] += cnt[find(a)]; // 需将a所属集合的大小加至b
p[find(a)] = find(b);
}
}7.3 维护到祖宗结点距离的并查集
public class DisjointSetWithDistance {
static final int N = 100010;
static int n;
static int[] p = new int[N];
static int[] d = new int[N]; // d[i]存储结点i到其根结点p[i]的距离
// 初始化
public static void init() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = i;
d[i] = 0; // 初始化全为0
}
}
// 并查集核心操作
public static int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
int u = find(p[x]); // u临时记录根结点
d[x] += d[p[x]]; // 更新x到根p[x]的路径长度
p[x] = u;
}
return p[x];
}
// 合并结点a和b所在集合:将a并至b
public static void union(int a, int b) {
p[find(a)] = find(b);
}
// 根据具体问题,初始化根find(a)的偏移量
public static void setDistance(int a, int distance) {
d[find(a)] = distance;
}
}8 堆
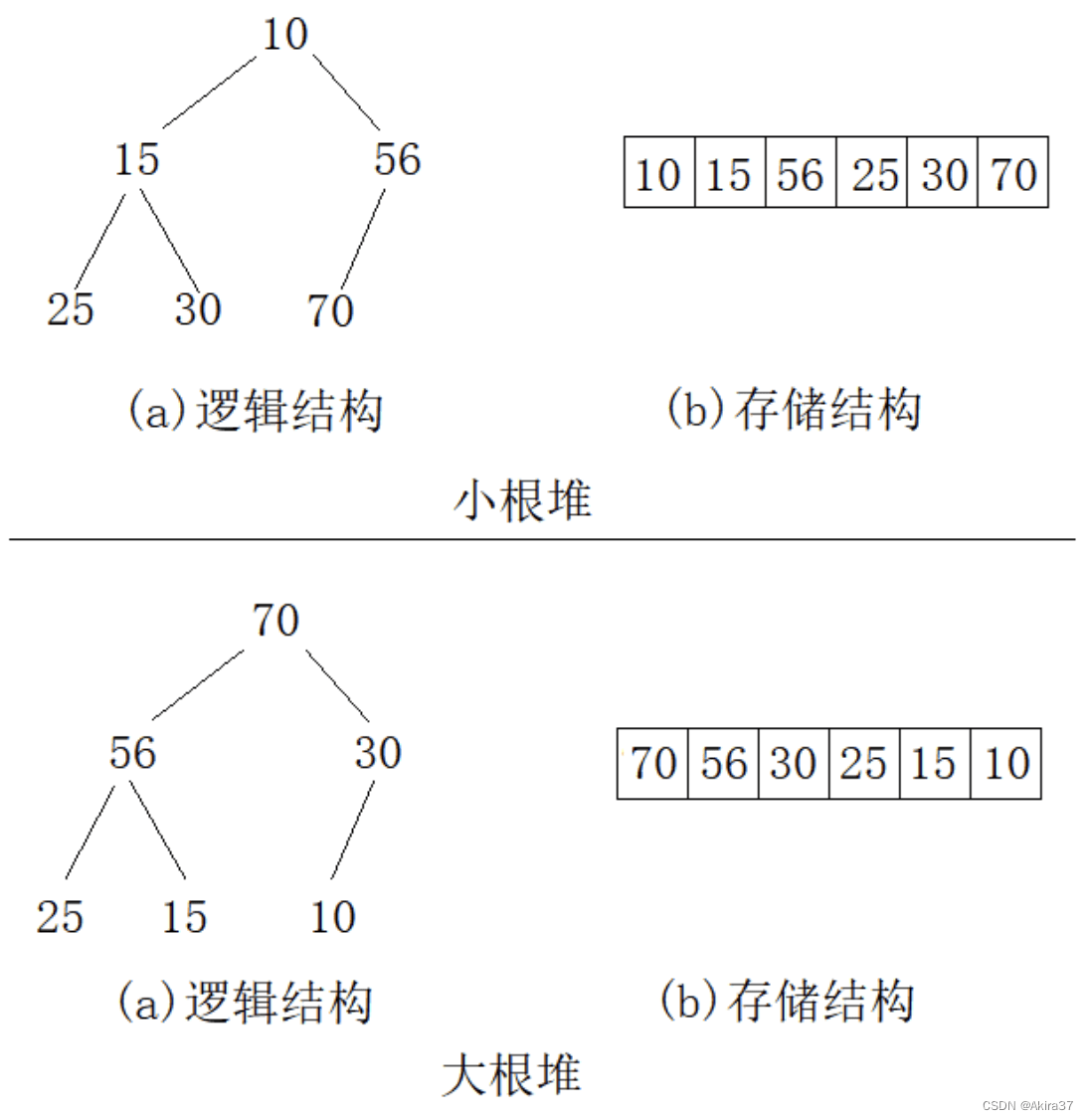
8.1 优先队列
java中PriorityQueue默认为小根堆,因此创建大根堆需要使用Collections.reverseOrder()作为构造参数
PriorityQueue<Integer> max_heap = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder()); // 大根堆()
PriorityQueue<Integer> min_heap = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 小根堆8.2 数组堆
可实现堆中任意元素的插入删除操作,并建立与插入序列之间的映射关系。
class Heap {
static final int N = 100010;
static int[] h = new int[N]; // 小根堆h[1 ... cnt],h[1]为堆顶/最小值,结点u的左右儿子(若存在)分别为2u、2u+1
static int cnt;
static int[] ph = new int[N]; // ph[k]映射插入序列中第k个点到堆中的下标u (Position-Heap)
static int[] hp = new int[N]; // hp[u]映射堆中结点u到插入序列中的序号k (Heap-Position)
static int idx = 0;
// 堆swap函数:交换堆中两个结点a和b的所有信息(若不建立映射则只需编写swap函数即可,略)
public static void heapSwap(int a, int b) {
// cpp:
// swap(ph[hp[a]], ph[hp[b]]);
// swap(hp[a], hp[b]);
// swap(h[a], h[b]);
}
// 向下调整:一路向下交换结点u与其较小的儿子
public static void down(int u) {
int t = u; // 记录u、2u、2u+1三个结点中的最小值结点编号
if (2 * u <= cnt && h[2 * u] < h[t]) {
t = 2 * u;
}
if (2 * u + 1 <= cnt && h[2 * u + 1] < h[t]) {
t = 2 * u + 1;
}
if (t != u) {
heapSwap(u, t);
down(t);
}
}
// 向上调整:一路向上交换结点u与其父结点
public static void up(int u) {
while (u / 2 != 0 && h[u / 2] > h[u]) {
heapSwap(u / 2, u);
u >>= 1;
}
}
// 插入一个数x
public static void insert(int x) {
cnt++;
idx++;
ph[idx] = cnt;
hp[cnt] = idx;
h[cnt] = x;
up(cnt);
}
// 删除最小值/堆顶元素
public static void removeTop() {
heapSwap(1, cnt);
cnt--;
down(1);
}
// 删除第k个插入的元素
public static void remove(int k) {
int u = ph[k];
heapSwap(u, cnt);
cnt--;
up(u); // up、down只会执行其中一个
down(u);
}
// 修改第k个插入的元素为x
public static void change(int k, int x) {
int u = ph[k];
h[u] = x;
up(u); // up、down只会执行其中一个
down(u);
}
}9 哈希
HashSet、HashMap
9.1 一般哈希
N最好取质数,使得冲突概率尽可能低
若要删除,则可额外开bool数组标记各地址元素状态来表示是否被删
9.1.1 拉链法
public class ChainingHashTable {
static final int N = 100010;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int idx = 0;
// 初始化
public static void init() {
Arrays.fill(h, -1);
}
// 向哈希表中插入一个数
public static void insert(int x) {
int t = (x % N + N) % N; // C++、Java的负数取余运算:(-n) mod k = -(n mod k)
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[t];
h[t] = idx++;
}
// 在哈希表中查询某个数是否存在
public static boolean find(int x) {
int t = (x % N + N) % N;
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) { // 遍历整条链表 h[t]
if (e[i] == x) return true;
}
return false;
}
}9.1.2 开放寻址法
数组长度应开到最大数据量的2~3倍
public class OpenAddressingHashTable {
static final int N = 100010;
static final int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // 若为INF则表示该哈希值的元素不在哈希表内
static int[] h = new int[N];
// 初始化
public static void init() {
Arrays.fill(h, INF); // 初始化为无穷
}
// 若x在哈希表中,返回x的下标;否则返回x应该插入的位置
public static int find(int x) {
int t = (x % N + N) % N;
while (h[t] != INF && h[t] != x) { // 若已存在该哈希值的元素且该元素不等于 x
t++;
if (t == N) {
t = 0; // 如果超出范围,则循环回到 0
}
}
return t; // 返回找到的位置
}
}9.2 字符串哈希
字符串前缀哈希法:快速判断两段字符串是否相等(不考虑冲突)
- 核心思想:将字符串看成 $P$ 进制数,$P$ 的经验值是 $131$ 或 $13331$ ,取这两个值的冲突概率极低
- 取模的数可选用$2^{62}-1$
public class StringHash {
static final int N = 100010;
static final long P = 131;
static final long MOD = (1L << 62) - 1;
static char[] str = new char[N]; // 待哈希字符串 str[0 ... n - 1]
static int n; // 字符串的长度
static long[] h = new long[N]; // h[k]存储字符串前k个字母的哈希值(前缀和)
static long[] p = new long[N]; // p[k]存储 P^k mod MOD
// 预处理前缀哈希
public static void init() {
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
h[i] = (h[i - 1] * P + str[i - 1]) % MOD; // 注意此处str从0开始索引
p[i] = p[i - 1] * P % MOD;
}
}
// 计算子串str[l ... r]的哈希值(注意h、p的定义)
public static long get(int l, int r) {
l++;
r++;
return (h[r] - h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1] % MOD + MOD) % MOD; // 注意防止h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1]为负
}
}